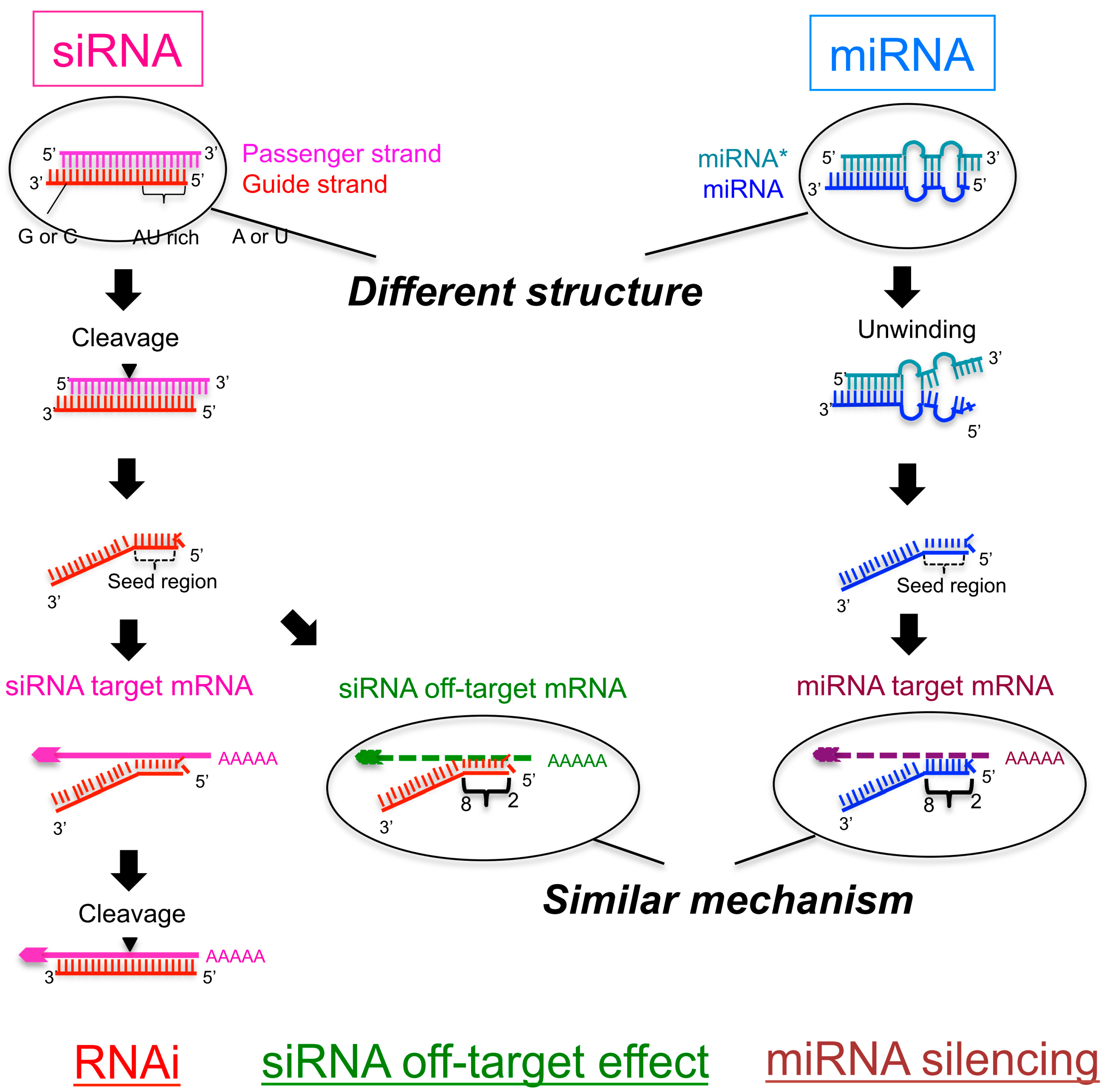
Although the seed region of siRNA is implicated in the miRNAlike offtarget effect, only some mRNAs, with this type of sequence complementarity, are silenced by siRNA By analogy, miRNAs regulate the expression of multiple mRNAs through binding of the seed region to the target 3′UTR, but not all mRNAs with the same degree of sequence complementarity are the targets of a givenThe nonseed region of siRNA was found to be subdivided into four domains, in which two nucleotide pairs (positions 13 and 14) were replaceable with cognate deoxyribonucleotides without reducing RNAi activity However, RNA sequences at positions 912 and 1518 were essential for effective gene silencing,Signature transcript 39 UTRs contain sequence complementarity to siRNA seed regions The indicated siRNAs were transfected into HeLa cells Gene expression signatures (pvalue #

Passenger Strand Cleavage Facilitates Assembly Of Sirna Into Ago2 Containing Rnai Enzyme Complexes Cell
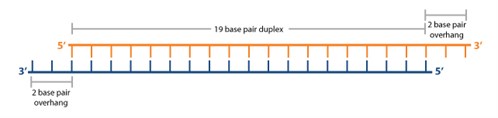
Seed region sirna
Seed region sirna-MISSION ® Predesigned siRNA were created using the proprietary Rosetta Inpharmatics siRNA Design algorithm in an exclusive partnership with Merck & Co The Rosetta siRNA Design Algorithm utilizes PositionSpecific Scoring Matrices and knowledge of the seed region to predict the most specific and effective sequences for your target genes · Alternatively, siRNA could cause "partial offtarget" (seed matching offtarget) effects, in cases where the designed siRNA seeding region (second to seventh position) matches with 3′UTR of offtarget, affecting its translation



Frontiers Thermodynamic Control Of Small Rna Mediated Gene Silencing Genetics
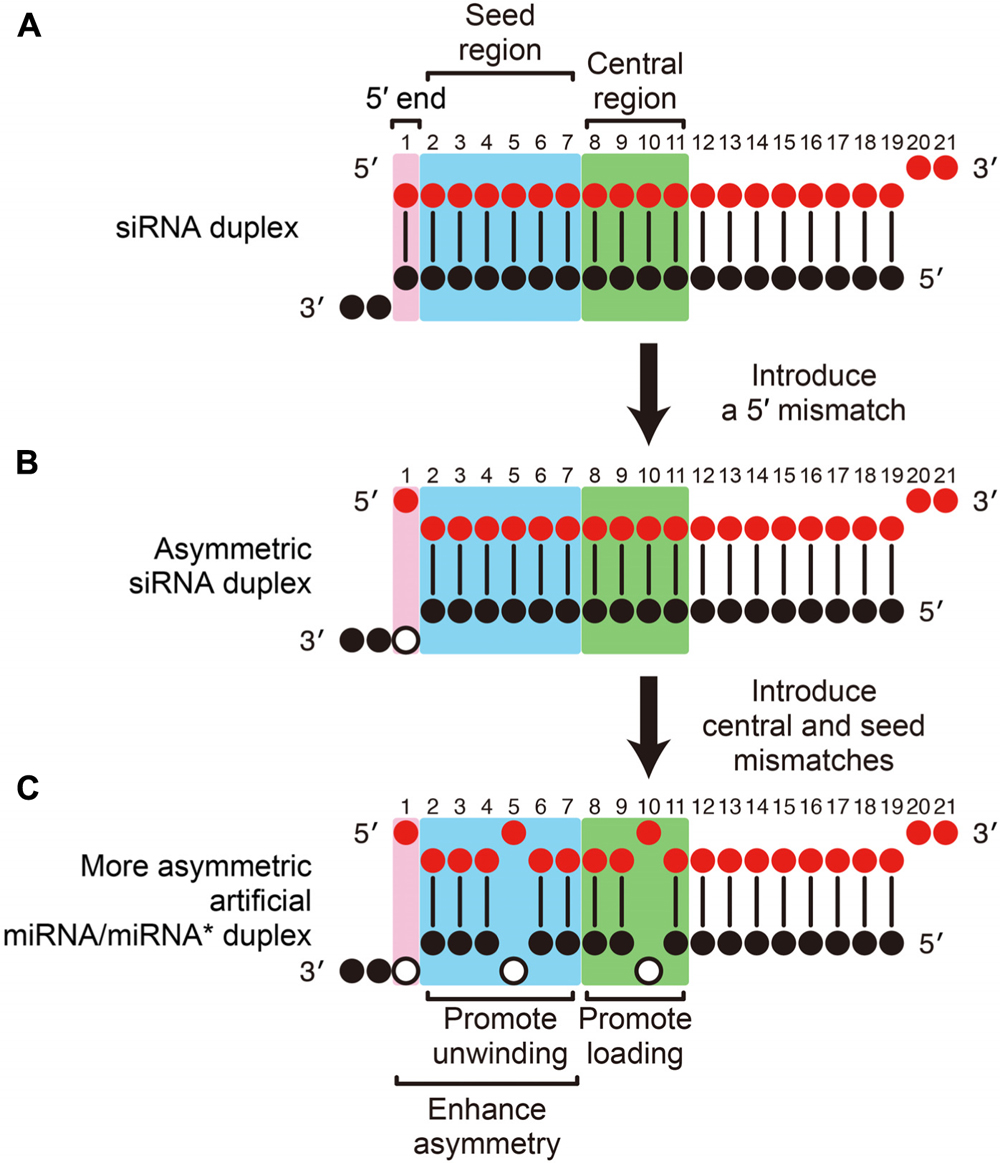
· Asymmetric replacement of seed region nucleotides with DNA bases has also been shown to reduce offtargeting as a result of seed region complementarity within the passenger strand Recent in vitro studies have shown that shRNA produces fewer offtarget effects than siRNASilencer Select siRNA modifications reduce offtarget effects and yield more reliable phenotypic data New bioinformatics techniques to decipher real positives from false positives that arise from the seed region have been highlighted in this publicationSiDirect selects siRNAs with lower Tm value at the seed region, which contains 7 nucleotides at positions 28 from 5′ end of the guide strand siRNAs downregulate many unintended genes whose transcripts have complementarities to the siRNA seed region
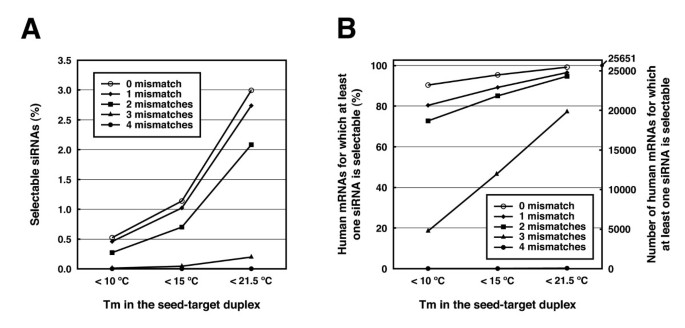
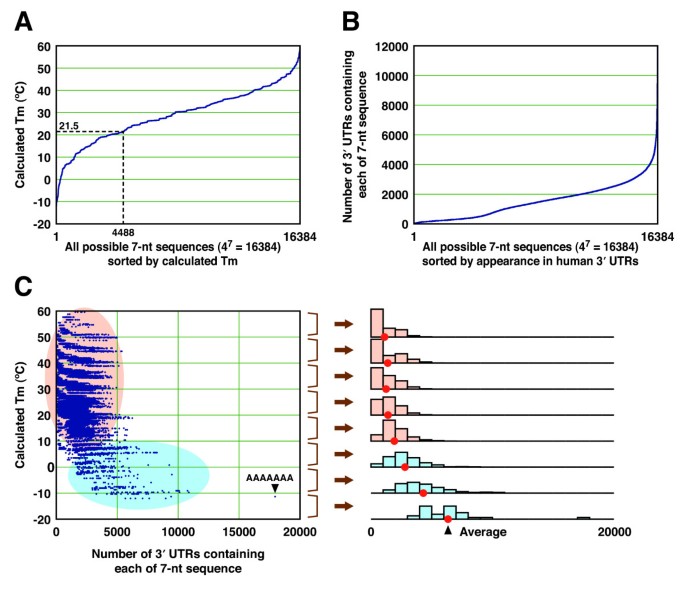
However, the addition of a fifth condition of low thermodynamic stability in the seed region to the siRNA selection criteria (i)– (iv) decreased the percentage of selectable siRNA candidates fromThe primary source of siRNAmediated offtargets is the seed region (nucleotides 27), which uses the microRNA pathway to induce nonspecific gene silencing via interactions within the 3' UTR Incorporating comprehensive bioinformatic strategies such as seed region filters and seed frequency analysis within the SMARTselection design strategy minimizes microRNAlike offYuan et al, 05) Thus, the seed region first identifies the target mRNAs, and subsequently form perfect basepairing with intended target mRNA and induce RNAi by Ago2
· This region, specifically nucleotides 2–7 at the 5′ end of the miRNA strand, is considered the "seed region" (Lewis et al 05) mRNA complementarity to the 3′ region of a miRNA is not generally required for miRNA function, but it is likely that additional complementarity to this region results in enhanced miRNAmediated downregulationSize of seed region of siRNA we proposed is 68 bases Functional alignment Besides general sequence alignment, GenScript siRNA design tool incorporates a novel alignment approach, functional alignment This idea for functional aligment derives from asymmetry of siRNA in the assembly of the RNAi enzyme complexHence, its silencing effect has been assumed to be extremely specific However, accumulated evidences revealed that siRNA could downregulate unintended genes with partial complementarities mainly to the sevennucleotide seed region of siRNA This phenomenon is



Compbio Sirna And Mirna




Rational Design Of Therapeutic Sirnas Minimizing Off Targeting Potential To Improve The Safety Of Rnai Therapy For Huntington S Disease Sciencedirect
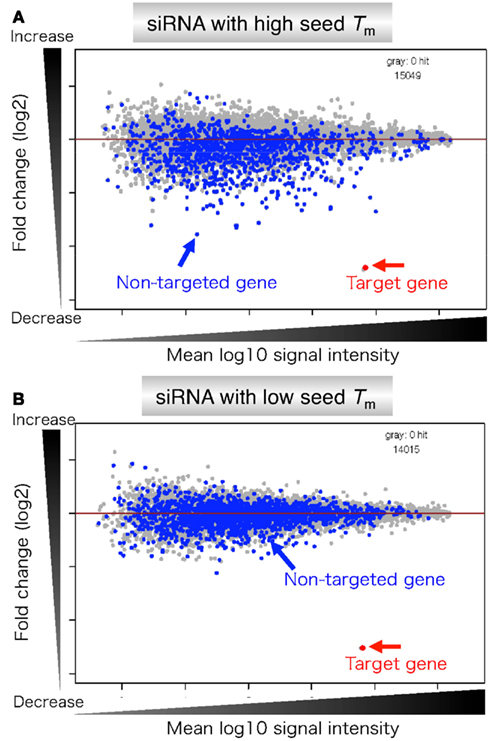
· Hence, because the siRNA seed region is a primary targetrecognition region, it is possible that the highly stable seedtarget duplex results in a strong siRNAWhen the siRNA seed region (2–8 nts from the 50 end of the guide strand) base pairs with the unintended genes 6–10 (Fig 1) The offtarget effect is considered to be induced by the similar molecular mechanismwithmiRNAmediatedRNAsilencing,whichdiffers from the mechanism of RNAiEnhance siRNA effectiveness Seed region filters and seed frequency analysis for siRNA designs to minimize offtarget effects ONTARGETplus modifications reduce the overall number of offtargets, and pooling reduces them even further Offtargets induced by the indicated siRNA



Www Tandfonline Com Doi Pdf 10 1080 14



Www Longdom Org Open Access Sdrna Sirna With A Dna Seed For An Efficient And Target Gene Specific Rna Interference Gnt Pdf
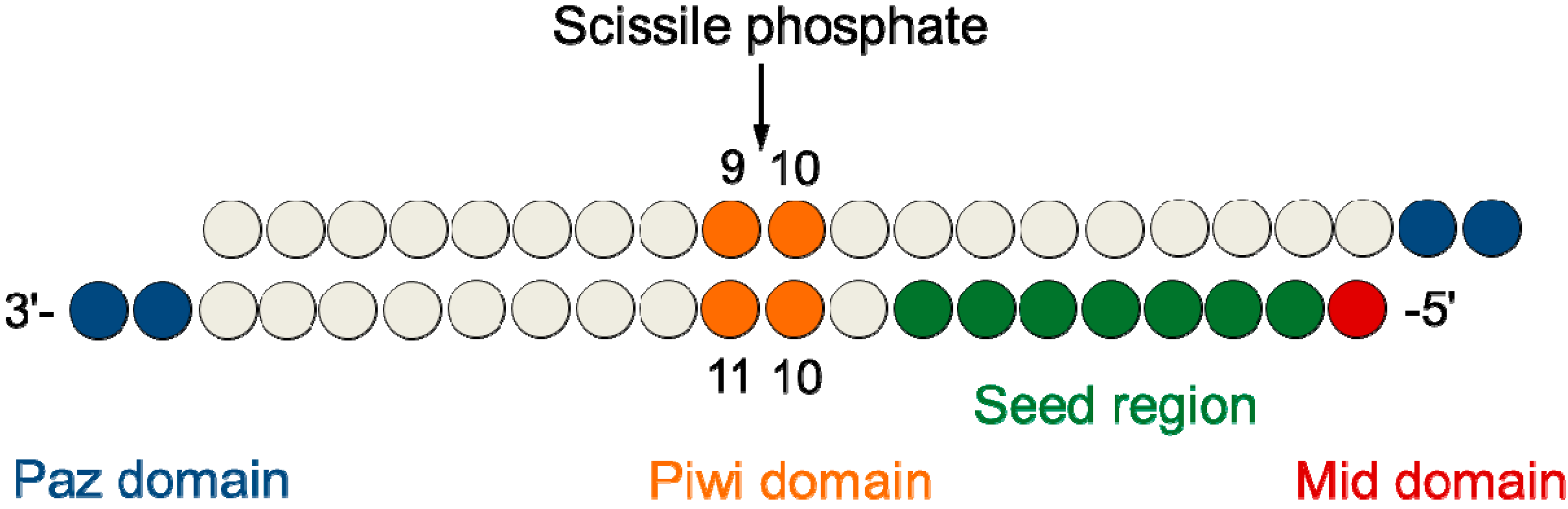
· The siRNA seed–3′ UTR match is only one parameter in what is assumed to be an extremely complex phenomenon Because the sheer number of genes that contain matches with any given siRNA seed regionSeed sequence region c) Unexpected toxicity siRNA produces cell toxicity either through general activation of the innate immune response or by affecting offtarget genes with a role in cell viability Example Federov et al (06) reported sequencedependent cell · The seed region is known to be situated on the surface of Ago in a quasihelical form to serve as the entry or nucleation site for small RNAs in the RISCs (Ma et al, 05;



Frontiers Mirna Like Duplexes As Rnai Triggers With Improved Specificity Genetics




Structures Of Sirna A And Dna Seed Containing Sirna B The Download Scientific Diagram
Our results confirm previous reports that strength of basepairing in the siRNA seed region is the primary factor determining the efficiency of offtarget silencing However, the degree of downregulation of offtarget transcripts with shared seed sequence is not necessarily similar, suggesting that there are additional auxiliary factors that influence the silencing potentialThrough SeedPairing Thermal Destabilization Figure 3 Destabilization of seedpairing to minimize microRNAlike offtarget effects Incorporation of a thermally destabilizing modification into the seed region of the antisense strand (red nucleotide) can reduce binding to seedbased offtargets and therefore increase ontarget specificityWidespread siRNA ''offtarget'' transcript silencing mediated by seed region sequence complementarity AIMEE L JACKSON, JULJA BURCHARD, JANELL SCHELTER, B NELSON CHAU, MICHELE CLEARY,



Sidirect 2 0 Updated Software For Designing Functional Sirna With Reduced Seed Dependent Off Target Effect Bmc Bioinformatics Full Text



Sirna Shrna Oligo Optimal Design
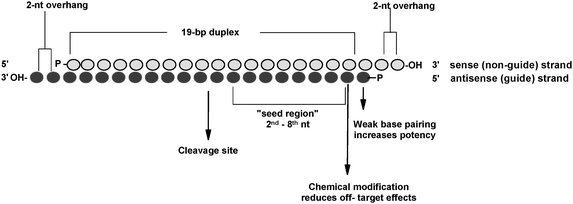
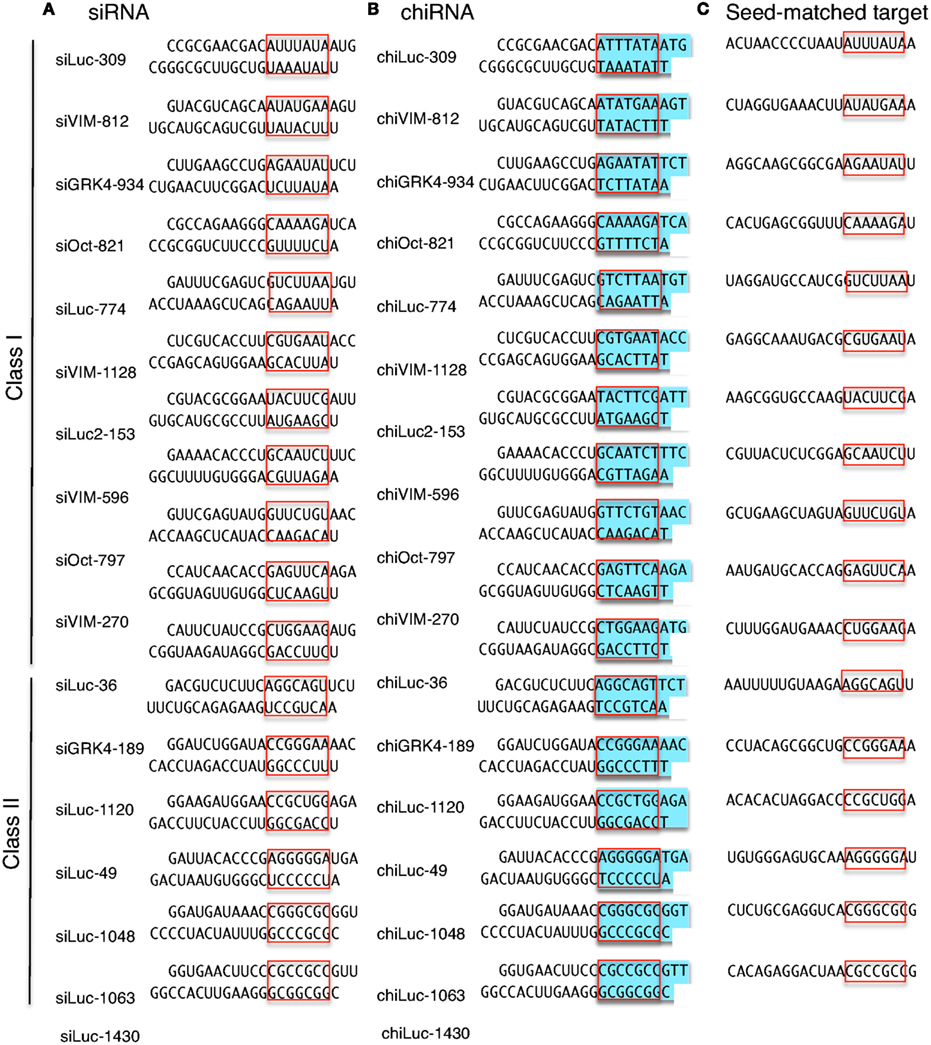
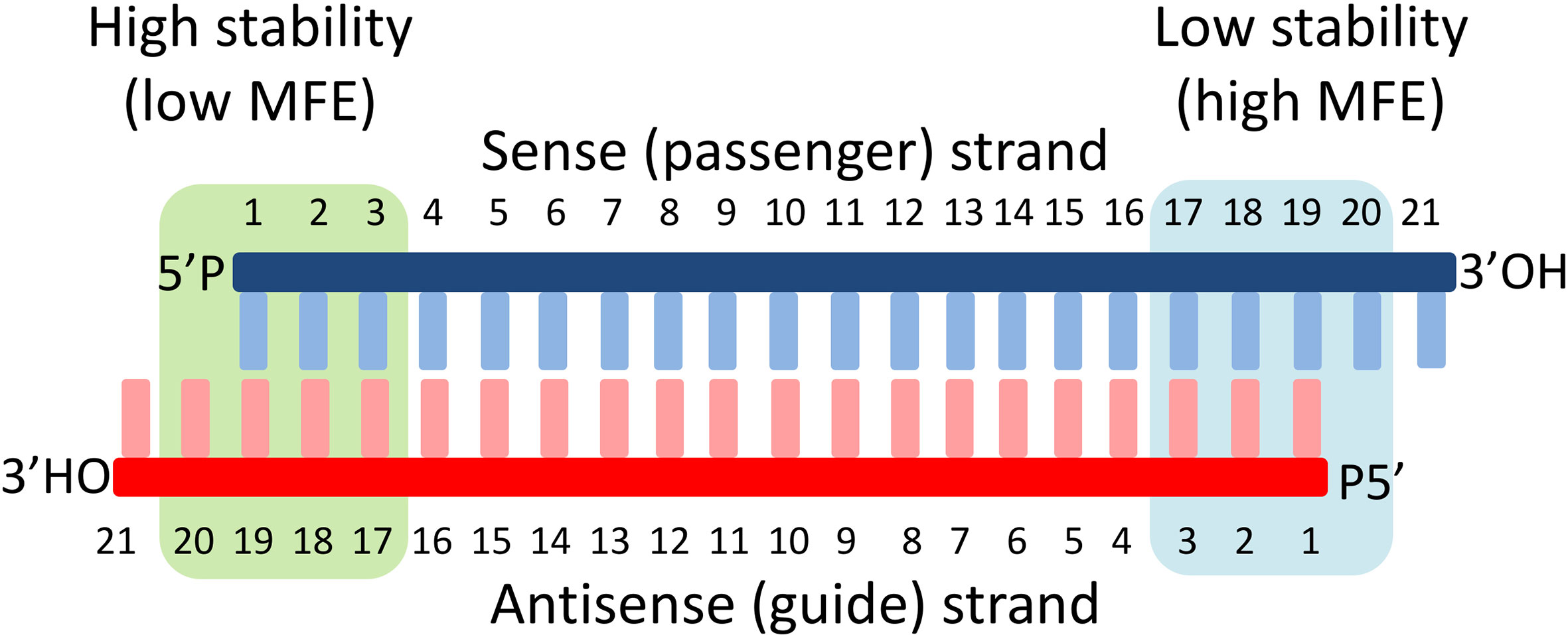
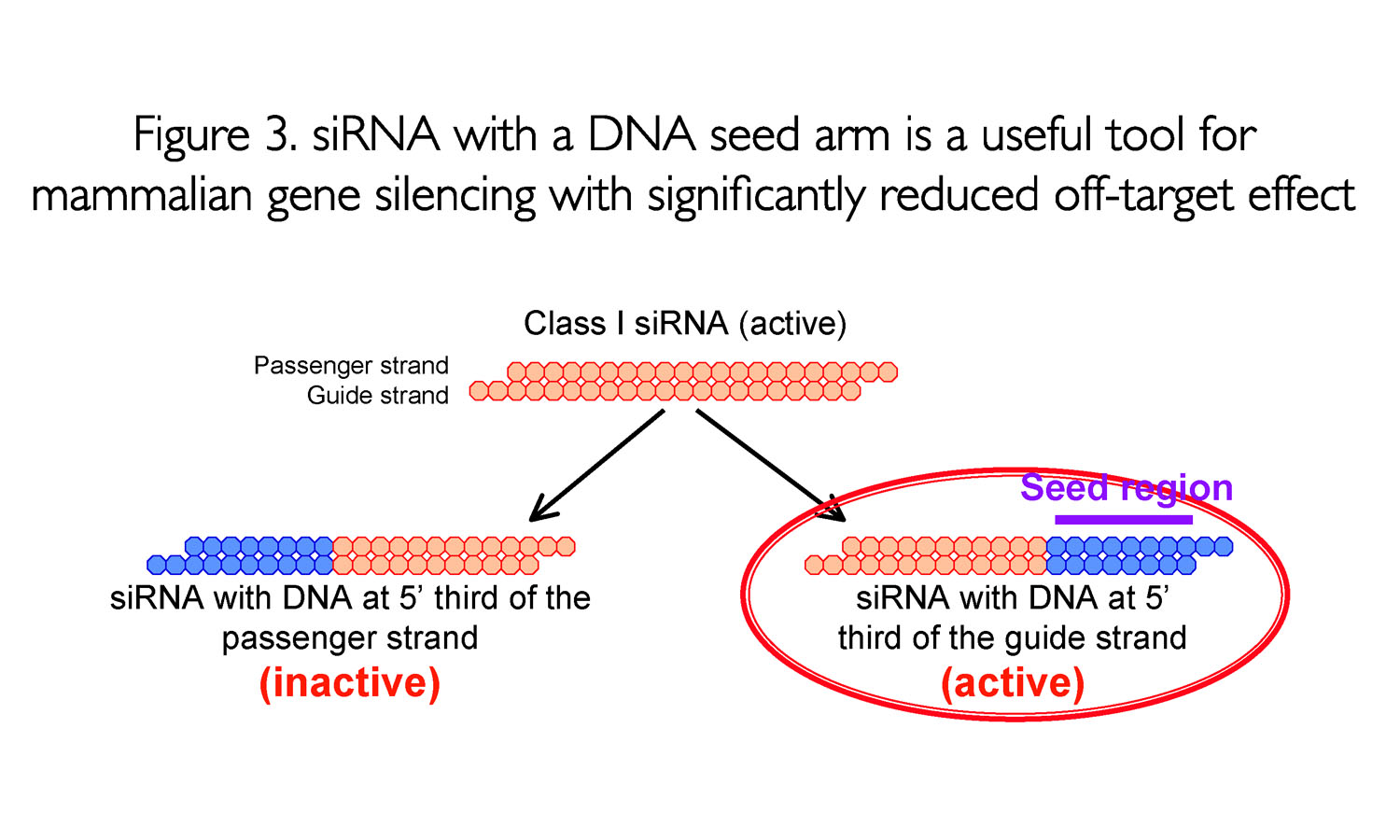
0214 · A highly functional siRNA may consist of two regions, the seed duplex region, which is capable of being totally replaced with DNA without substantial loss of gene silencing activity, and the nonseedduplex region, most of which should be RNA and possibly provide binding sites for RNAbinding RLC/RISC proteinsImportance of seed complement frequency to siRNA specificity RNA 14, 853–861 (08) Characterization of the microRNA seed region, nucleotides 2–6 of the siRNA antisense strand, predicts that nucleotide identity of this region may allow the siRNA to act through the microRNA pathway3–5 Thus, a negative controlRecognition of the mRNA target by RISC* occurs in several stages, wherein the "seed" region (the siRNA region from 2 to 8 nucleotides from the 5′ end of antisense strand) plays an important role




Passenger Strand Cleavage Facilitates Assembly Of Sirna Into Ago2 Containing Rnai Enzyme Complexes Cell



Www Alnylam De Wp Content Uploads 17 09 Ots 17 Poster 2 Vasant Et Al Pdf
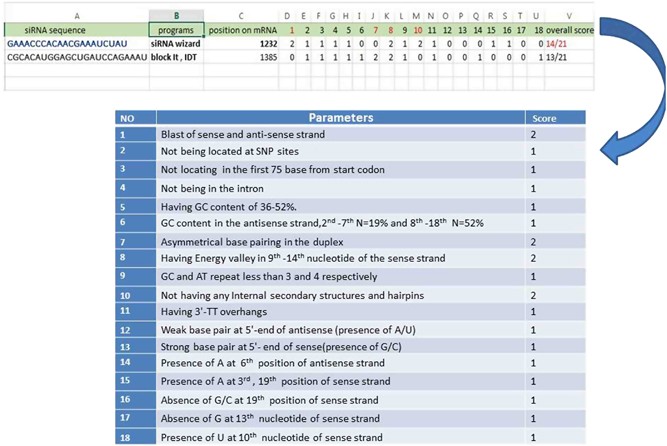
To avoid off target effect, siRNA Wizard filter candidate siRNA sequence to remove sequence displaying a known miRNA SEED recognition region at 3' end Loop for short hairpin siRNAs (shRNA) We and others have tested a variety of sequences for the loop between the two complementary regions of a shRNA, ranging from 3 to 9 nt in length · Widespread siRNA "offtarget" transcript silencing mediated by seed region sequence complementarity Organism Homo sapiens Experiment type Expression profiling by array Summary Transfected siRNAs and miRNAs regulate numerous transcripts that have only limited complementarity to the active strand of the RNA duplexSmartBase TM siRNA Recommended Modifications 1 Alternating 2'F bases and 2'OMe bases in siRNA enhances duplex stability and are more resistant to RNase degradation 2 Use a few 2'OMe bases in the seed region of the guide strand to decrease the Tm below 215 of this region 2'O methyl base hybridization with RNA has a lower TM



Precise And Efficient Sirna Design A Key Point In Competent Gene Silencing Cancer Gene Therapy
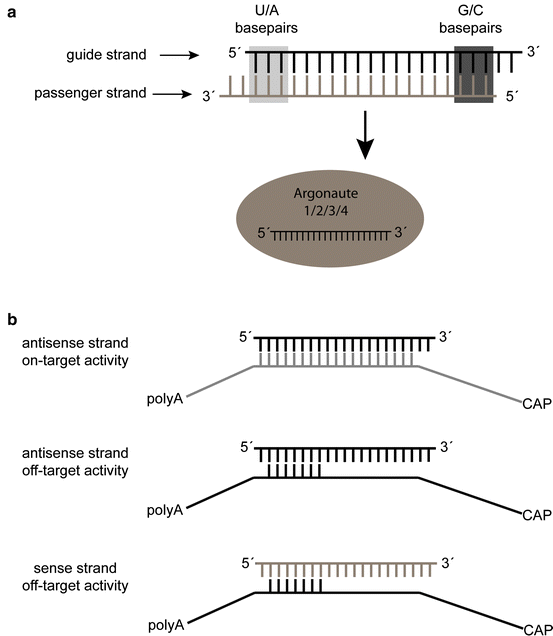



Sirna Design Principles And Off Target Effects Springerlink
The seed region of siRNA guide strand and target mRNA (seedtarget duplex) (Figure 1a) 12 Furthermore, we have developed a DNARNA chimeric siRNA (chiRNA) with deoxyribonucleotides in the 5' proximal eight nucleotides of the guide strand and the complementary nucleotides The chiRNA showed virtually no offtarget effects,Seed region The chemical modifications of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), PS, and DNA−PS were introduced into all of the seven nucleotides of the seed region of the siRNA guide strand (Figure 2b) In addition, 3 (positions 4−6), 5 (positions 3−7),Silencer Select siRNA modifications reduce offtarget effects and yield more reliable phenotypic data New bioinformatics techniques to decipher real positives from false positives that arise from the seed region have been highlighted in this publication




6mer Seed Toxicity Determines Strand Selection In Mirnas Biorxiv
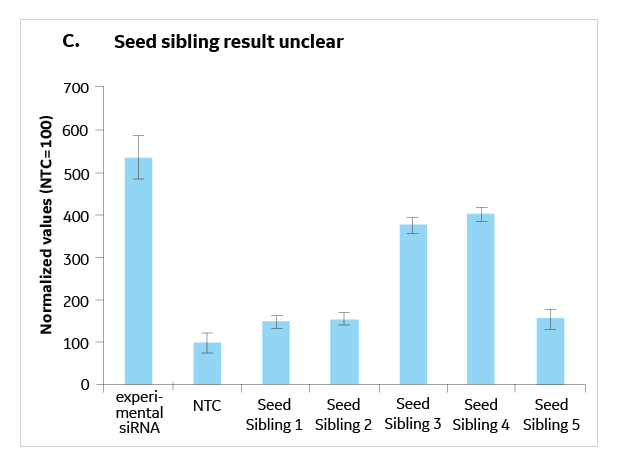



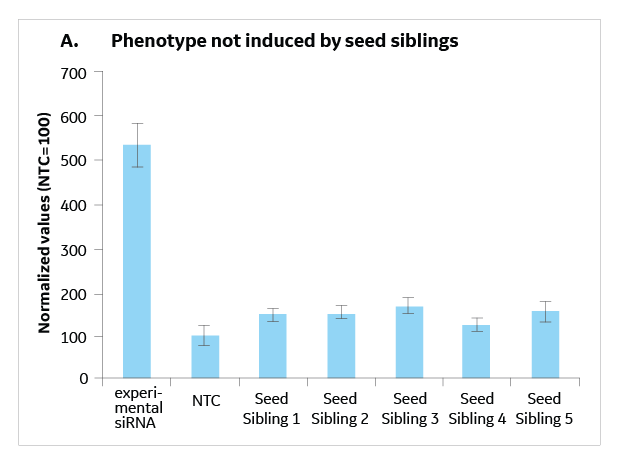
Seed Sibling Controls For Rnai Hit Validation
The siRNA Workflow A typical siRNA experiment (Figure 2) starts with the selection of a gene target and ends in the determination of knockdown efficiency, which is interpreted with respect to the objectives of the experimentFor studies that are focused on individual gene targets, there may be a variety of decisionmaking steps involved, as well as process optimization requirementsSiRNA recognition of the target mRNA is conferred by the "seed region", a six nucleotide stretch corresponding to positions 27 on the antisense siRNA strand After the siRNA seed region anneals, the catalytic RNase H domain of Argonaute then subjects perfectly complementary mRNA sequences 10 nucleotides from the 5' end of the incorporated siRNA strand to nucleolyticSeedbased offtarget effects A, seed region of Pik3ca siRNA B, cluster plots showing seeds enriched in 3' UTRs of downregulated genes after transfection with unmodified (B) or 2'Omethyl modified Pik3ca siRNA The "aaagcc"seed sequence remains enriched after chemical modification (Source Rasmussen et al,13)



Www Sitoolsbiotech Com Pdf Waystoreduceofftargets2 Pdf




Functional Sirna Sequence And The Mechanism Of Rnai Without Off Target Download Scientific Diagram
化学合成siRNA siRNA(small interfering RNA)とは、21~23塩基対からなる低分子二本鎖RNAです。 siRNAはRNAiと呼ばれる現象に関与しており、mRNAの切断によって配列特異的に遺伝子の発現を抑制します。 細胞内に導入されたsiRNAは、二本鎖のうちの一本鎖(アンチSelection of Chemical Modifications in the siRNA Seed Region That Repress OffTarget Effect Yoshiaki Kobayashi, Kengo Miyamoto, Misako Aida, Kumiko UiTei Pages 1730 StickBased Methods for AptamerMediated siRNA Targeted Delivery Silvia Catuogno, Carla Lucia Esposito, Paloma H GiangrandeCompared with an siRNAlike approach, the requirement of perfect complementarity of the microRNA seed region to a given target sequence in the microRNA/target model has proven to be a more efficient strategy, accomplishing the selective targeting of
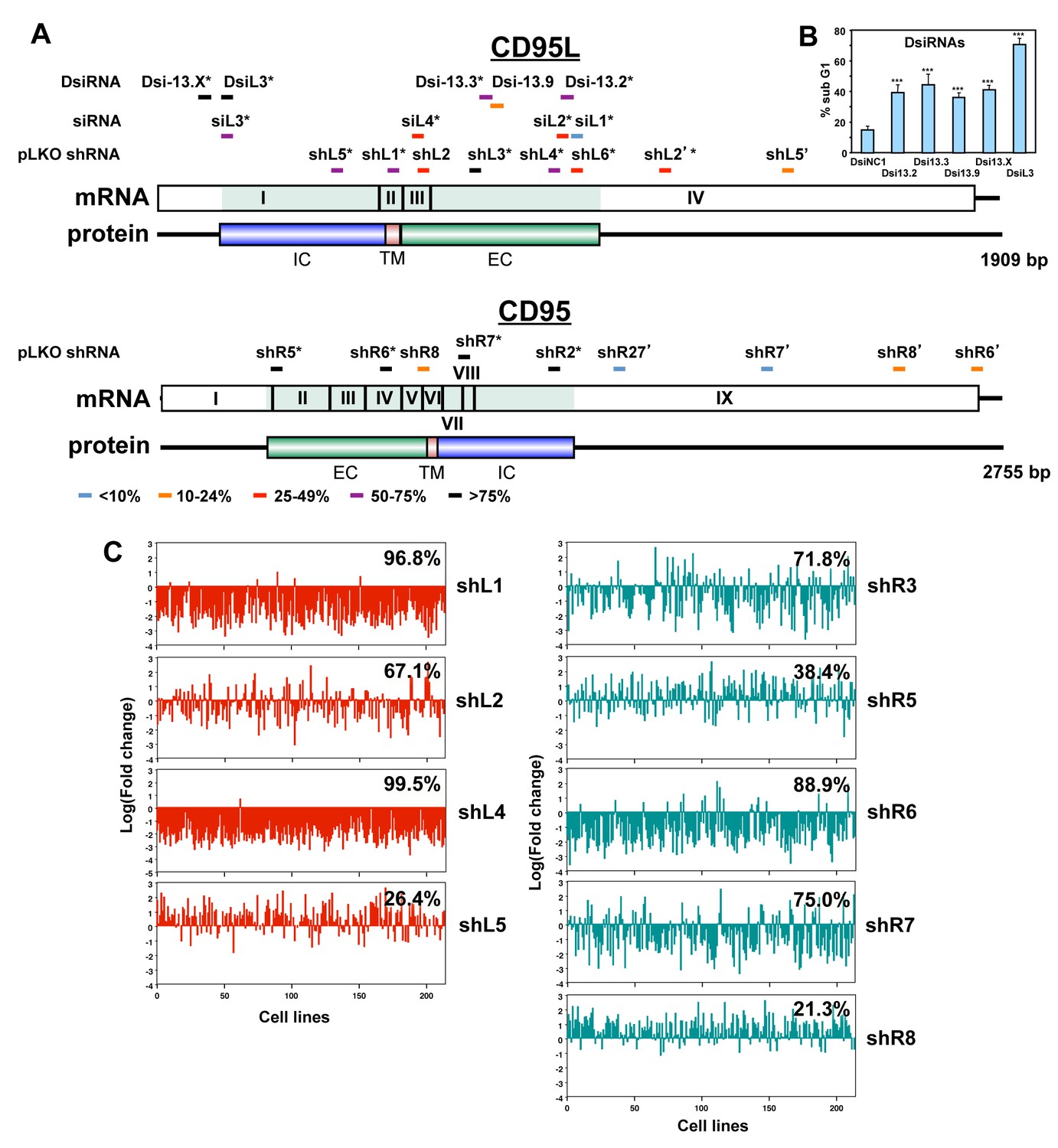



Many Si Shrnas Can Kill Cancer Cells By Targeting Multiple Survival Genes Through An Off Target Mechanism Elife
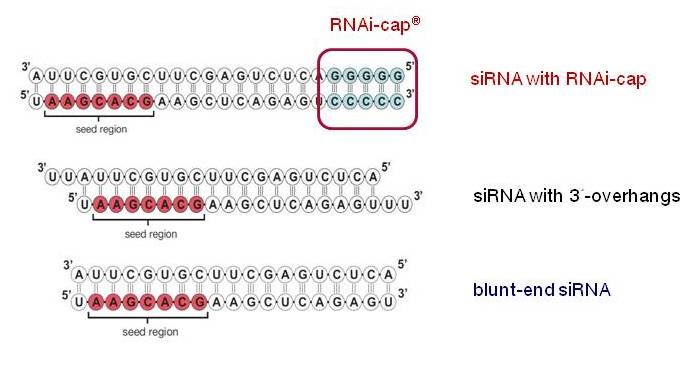



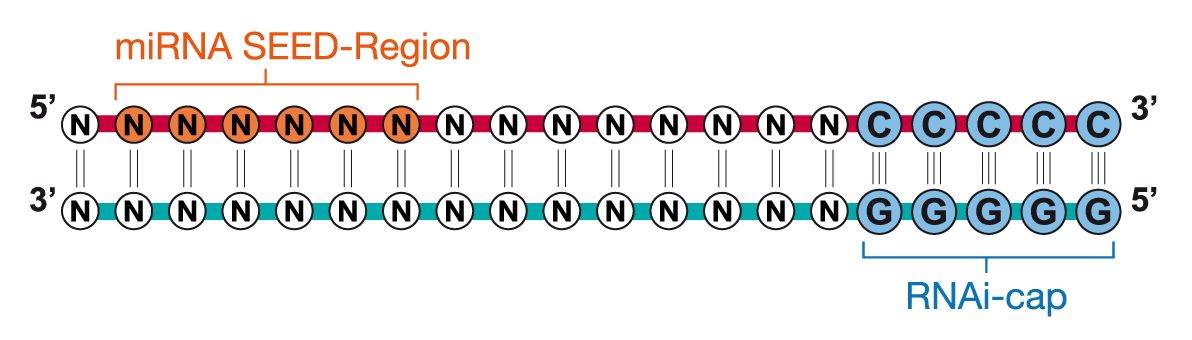
Riboxx Rna Technologies Benefits Of Rnai Cap For Sirna
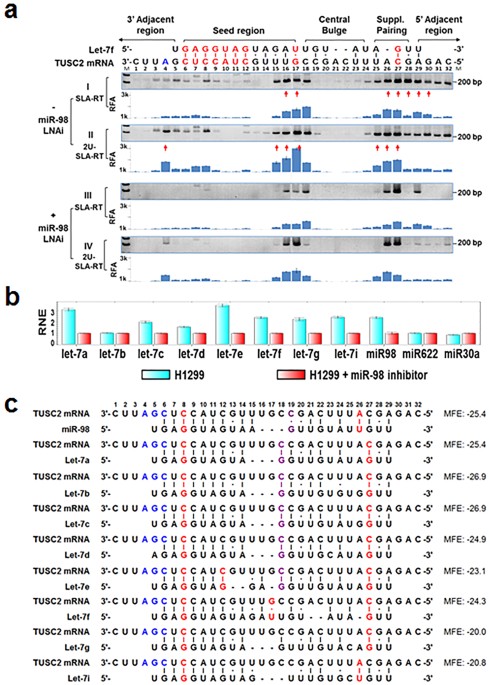
· Although littletono basepairing is usually observed between siRNA nonseed region (nucleotides 9– in Fig 1C) and the corresponding offtarget region, it was previously reported with miRNAs that such partial basepairing is an additional factor that influences the efficiency of seeddependent knockdown 18 , and was thus included in our analysisThe seed sequence or seed region is a conserved heptametrical sequence which is mostly situated at positions 27 from the miRNA 5´end Even though base pairing of miRNA and its target mRNA does not match perfect, the "seed sequence" has to be perfectly complementary · Clearly, the seed sequences of miRNA (identified with miRNA databases) should be avoided in siRNA design 69 In addition, the siRNA should have a low thermodynamic stability of the duplex between the seed region of the guide strand of siRNA and its target mRNA, since a low seedtarget duplex stability reduces the capability of siRNA to induce seeddependent off



Sidirect 2 0 Updated Software For Designing Functional Sirna With Reduced Seed Dependent Off Target Effect Bmc Bioinformatics Full Text



Www Longdom Org Open Access Sdrna Sirna With A Dna Seed For An Efficient And Target Gene Specific Rna Interference Gnt Pdf
1910 · 3' UTR/seed region analysis Several studies have shown that offtarget effects may be caused by matches of the seed region of the siRNA antisense strand with the 3' untranslated region of unintended mRNA targets (see table) The seed region comprises 6 nucleotides in positions 2–7 of the antisense siRNA strand of the siRNA duplex · siRNA seed regions preferentially align with the 3′ UTR regions of unintended transcripts (Upper panels) 36 siRNAs were aligned by FASTA to their downregulated offtarget signature transcripts and to a background set of 10,631 transcript sequences with mapped CDS · Such offtarget effect is an undesirable adverse effect for knocking down a target gene specifically Here we describe the powerful strategy to avoid offtarget effects without affecting the RNAi activity by the introduction of DNA or 2′Omethyl modifications in the siRNA seed region




Sidirect 2 0 Updated Software For Designing Functional Sirna With Reduced Seed Dependent Off Target Effect Bmc Bioinformatics Full Text




Seedseq Off Target Transcriptome Database
SiRNA designs with lowfrequency seed regions ensure fewer offtargets SMARTpool siRNA reagents improve specificity when retaining high potency 5' 3' 3' 5' Antisense Strand Sense Strand seed region of antisense strand (positions 27) 100 80 60 40 0 Low Medium High Seed Frequency Class Number of OffTargets



Biological And Physicochemical Characterization Of Sirnas Modified With 2 2 Difluoro 2 Deoxycytidine Gemcitabine New Journal Of Chemistry Rsc Publishing




Pdf New Algorithm For Analysis Of Off Target Effects In Sirna Screens Semantic Scholar




A The Structure Of Sirna Sense And Antisense Strands And Target Mrna Download Scientific Diagram




Rna Interference Moss Major Reference Works Wiley Online Library



1




Sirna Versus Mirna As Therapeutics For Gene Silencing Sciencedirect



Microrna Mediated Target Mrna Cleavage And 3 Uridylation In Human Cells Scientific Reports



1



Frontiers Thermodynamic Control Of Small Rna Mediated Gene Silencing Genetics




Small Interfering Rna Wikipedia




Research Ui Tei Lab The University Of Tokyo



Www Longdom Org Open Access Sdrna Sirna With A Dna Seed For An Efficient And Target Gene Specific Rna Interference Gnt Pdf




Pdf Interfering With Disease A Progress Report On Sirna Based Therapeutics Semantic Scholar




Selection Of Chemical Modifications In The Sirna Seed Region That Repress Off Target Effect Springerlink
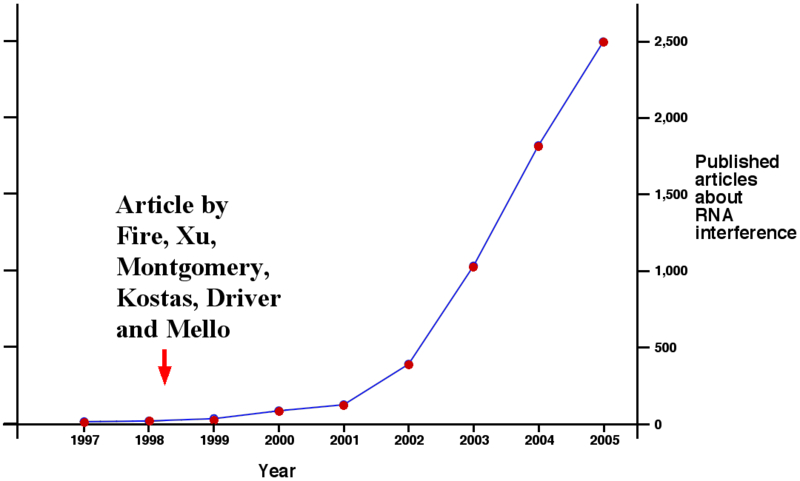



Small Interfering Rna Sirna Mcmanus Lab




Frontiers Thermodynamic Control Of Small Rna Mediated Gene Silencing Genetics



Small Interfering Rna Sirna Mcmanus Lab




Graphical Representation Of Sirna Molecule A Sirna Duplex With Download Scientific Diagram




Ago Accessible Anticancer Sirnas Designed With Synergistic Mirna Like Activity Molecular Therapy Nucleic Acids
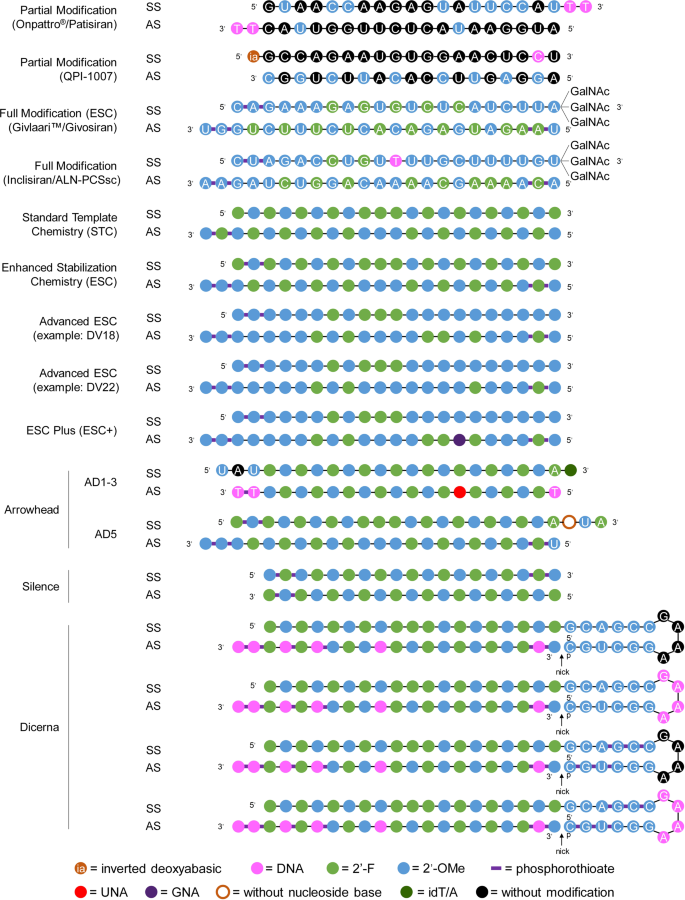



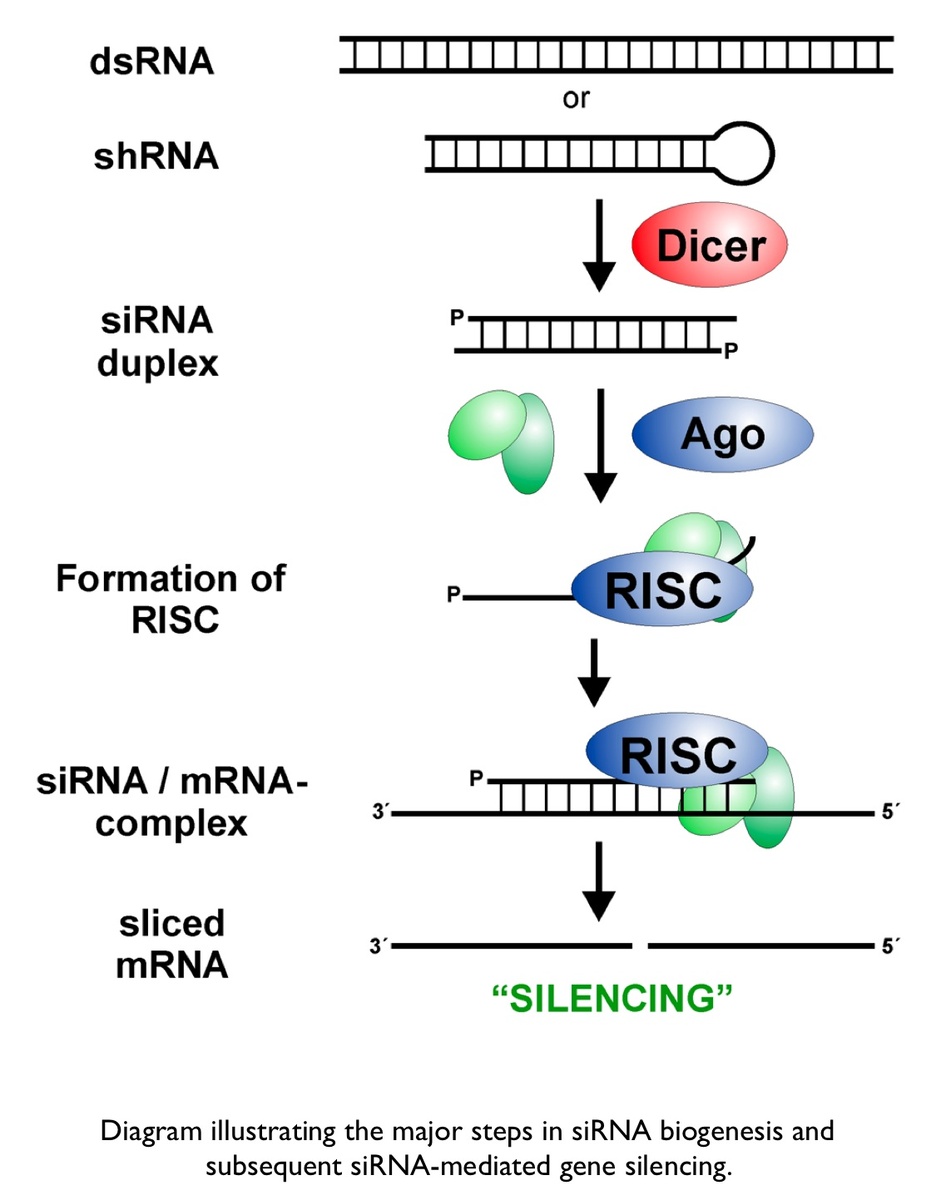
Therapeutic Sirna State Of The Art Signal Transduction And Targeted Therapy
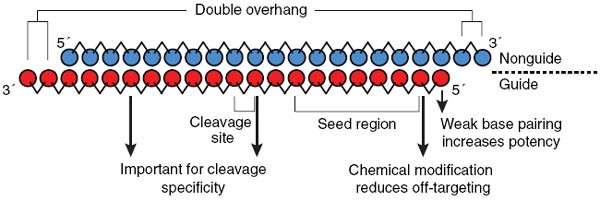



Rnai Therapeutics A Potential New Class Of Pharmaceutical Drugs Nature Chemical Biology
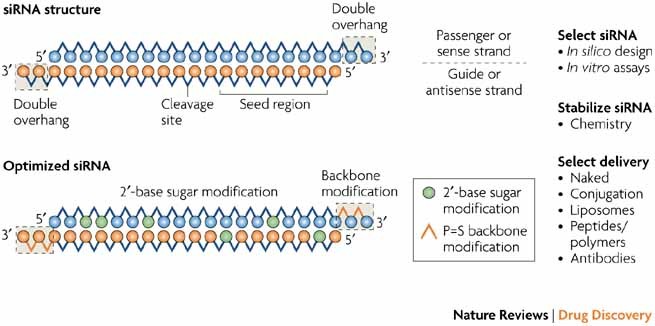



Interfering With Disease A Progress Report On Sirna Based Therapeutics Nature Reviews Drug Discovery
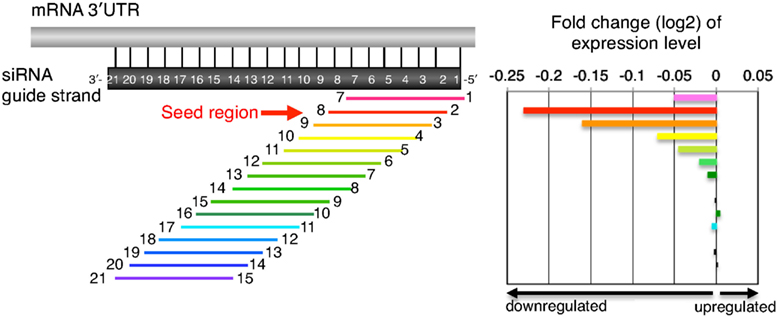



Frontiers Thermodynamic Control Of Small Rna Mediated Gene Silencing Genetics




Clinical Development Of Synthetic Sirna Therapeutics Sciencedirect




Significant Seed Region Based Off Target Activity Is Induced By Sirna Download Scientific Diagram




Effective Gene Silencing Activity Of Prodrug Type 2 O Methyldithiomethyl Sirna Compared With Non Prodrug Type 2 O Methyl Sirna Sciencedirect
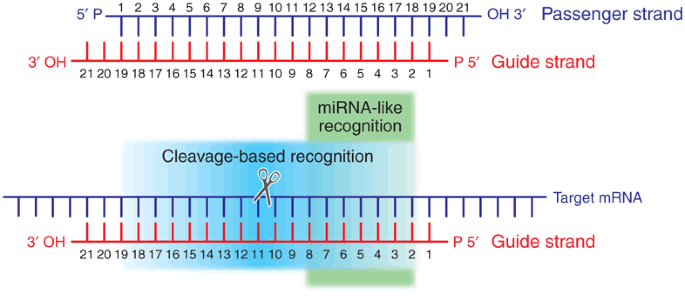



On The Art Of Identifying Effective And Specific Sirnas Nature Methods



1
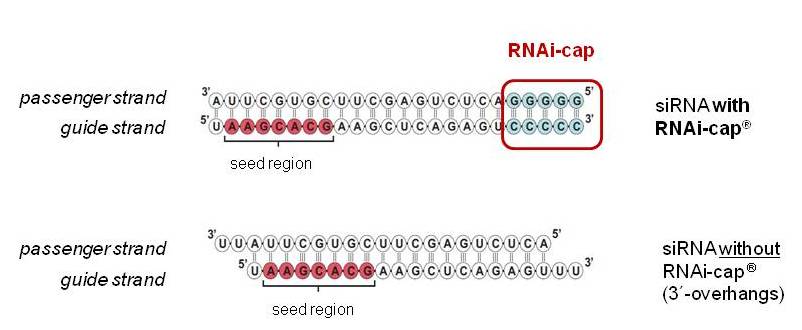



Riboxx Rna Technologies Better Silencing With Rnai Cap



Ijms Free Full Text Is The Efficiency Of Rna Silencing Evolutionarily Regulated Html




6mer Seed Toxicity In Tumor Suppressive Micrornas Biorxiv



Frontiers Sirna Finder Si Fi Software For Rnai Target Design And Off Target Prediction Plant Science



1



Http Ui Tei Rnai Jp Assets Files Pdf 17iribe Acsomega Pdf




2 O Methyl At Mer Guide Strand 3 Termini May Negatively Affect Target Silencing Activity Of Fully Chemically Modified Sirna Sciencedirect




Figure 1 From Sdrna Sirna With A Dna Seed For An Efficient And Target Gene Specific Rna Interference Semantic Scholar



Www Sitoolsbiotech Com Pdf Waystoreduceofftargets2 Pdf




Seedseq Off Target Transcriptome Database



Molecules Free Full Text Modulation Of The Rna Interference Activity Using Central Mismatched Sirnas And Acyclic Threoninol Nucleic Acids Atna Units Html



Research Ui Tei Lab The University Of Tokyo




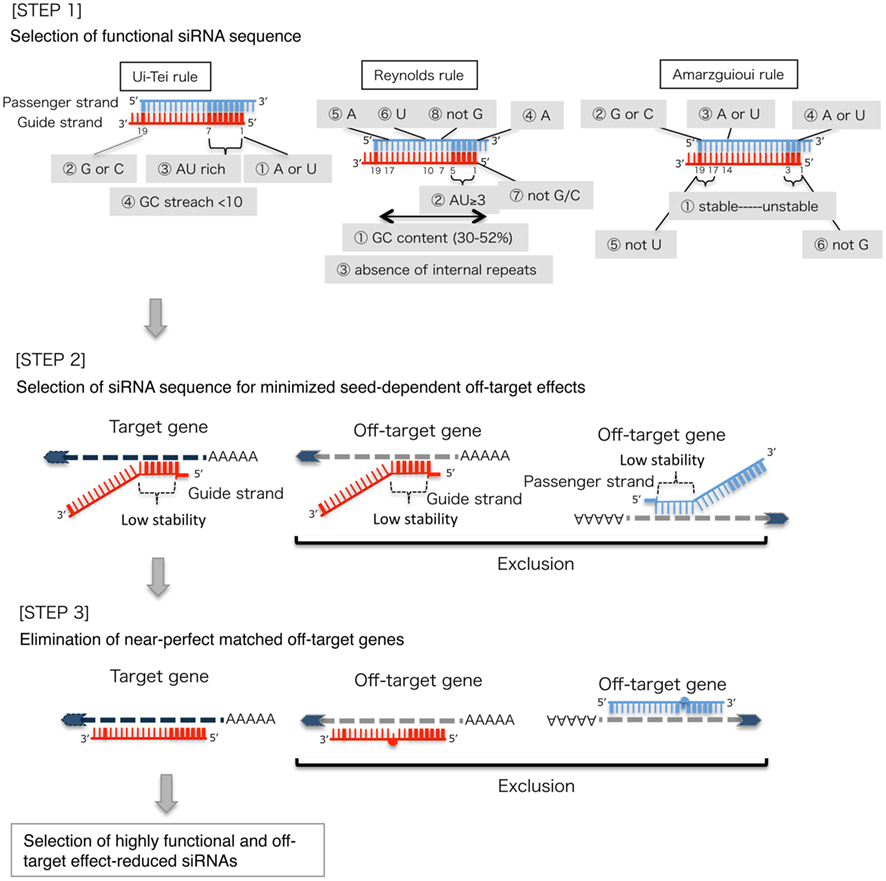
Frontiers Sirna Design Software For A Target Gene Specific Rna Interference Genetics




Figure 5 From Rnai For Treating Hepatitis B Viral Infection Semantic Scholar



Smt0nozelyyshm



Sirna And Rnai Pricelist From Gene Link




Rational Design Of Highly Efficient Artificial Mirna Mirna Download Scientific Diagram




Selective Targeting Of Point Mutated Kras Through Artificial Micrornas Pnas



The Sirna Non Seed Region And Its Target Sequences Are Auxiliary Determinants Of Off Target Effects Document Gale Academic Onefile




Pdf Interactions Between The Non Seed Region Of Sirna And Rna Binding Rlc Risc Proteins Ago And Trbp In Mammalian Cells



Http Ui Tei Rnai Jp Assets Files Pdf 17iribe Acsomega Pdf



Simax Sirna



The Sirna Non Seed Region And Its Target Sequences Are Auxiliary Determinants Of Off Target Effects



Sirna And Rnai Pricelist From Gene Link



The Sirna Non Seed Region And Its Target Sequences Are Auxiliary Determinants Of Off Target Effects




Sirnas And Shrnas Tools For Protein Knockdown By Gene Silencing




Gene Silencing By 2 O Methyldithiomethyl Modified Sirna A Prodrug Type Sirna Responsive To Reducing Environment Sciencedirect



Riboxx Rna Technologies Benefits Of Rnai Cap For Mirna



Frontiers Sirna Design Software For A Target Gene Specific Rna Interference Genetics
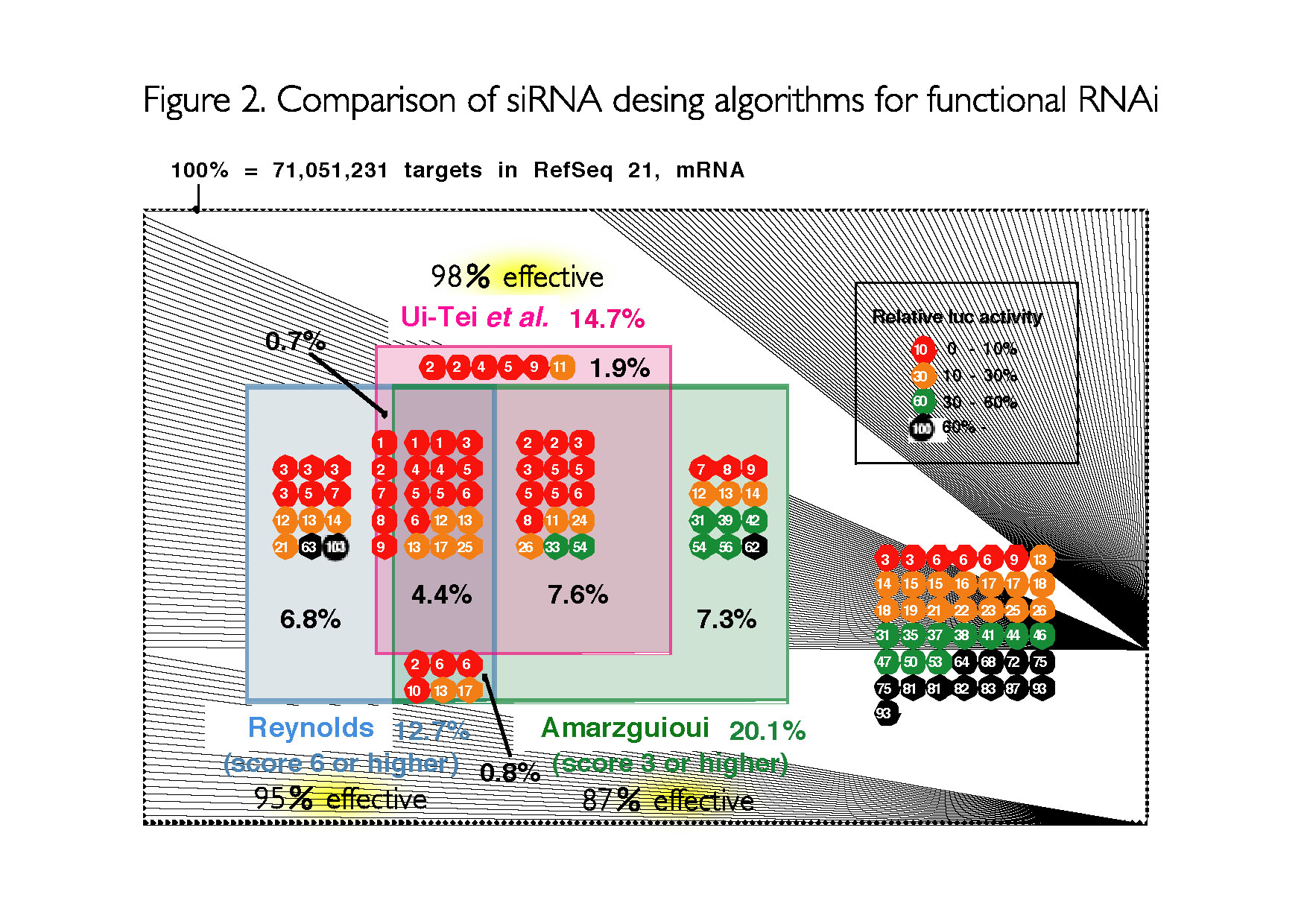



Research Ui Tei Lab The University Of Tokyo
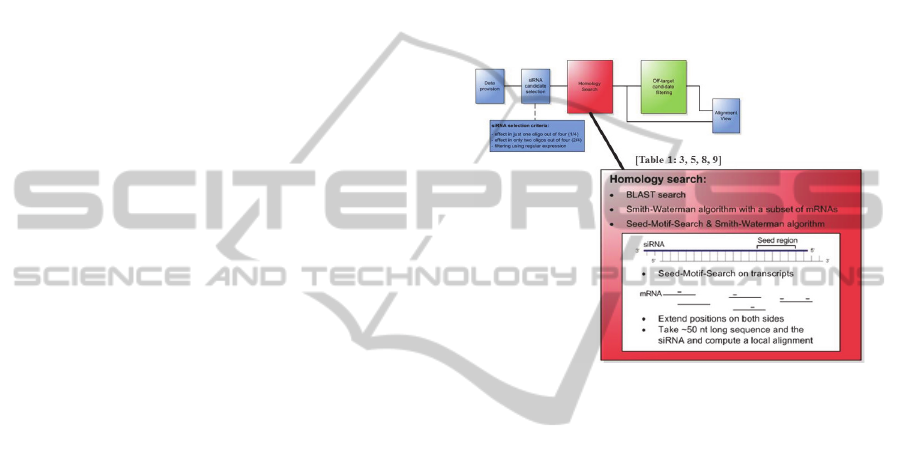



New Algorithm For Analysis Of Off Target Effects In Sirna Screens
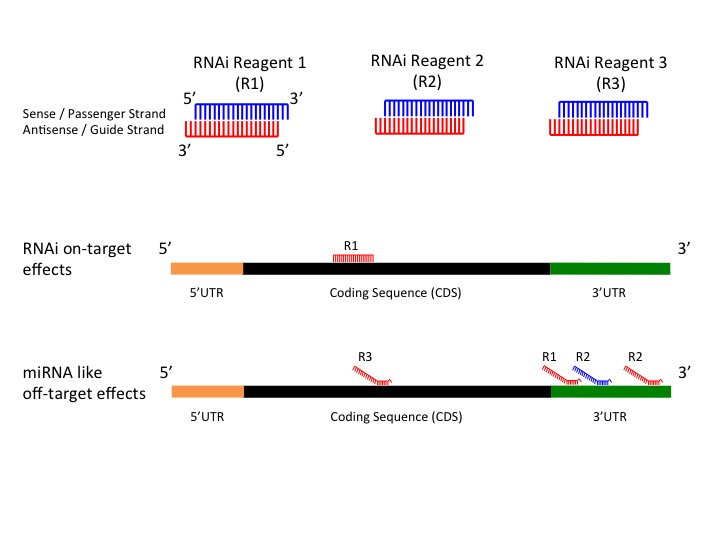



Gess
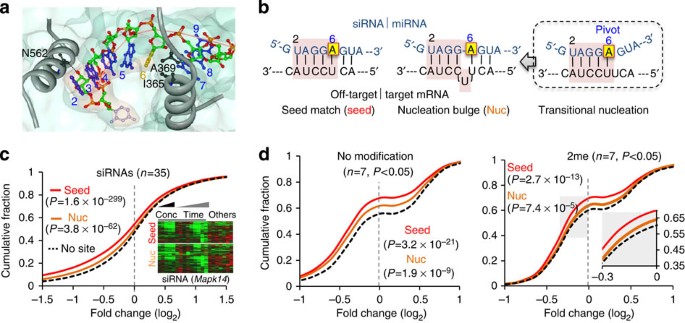



Abasic Pivot Substitution Harnesses Target Specificity Of Rna Interference Nature Communications




Abundant Expression Of Maternal Sirnas Is A Conserved Feature Of Seed Development Pnas
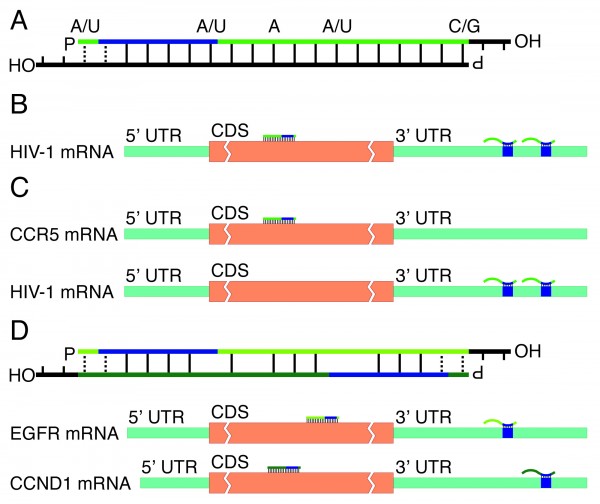



Unconventional Rna Interference Recent Approaches To Robust Rnai European Pharmaceutical Review
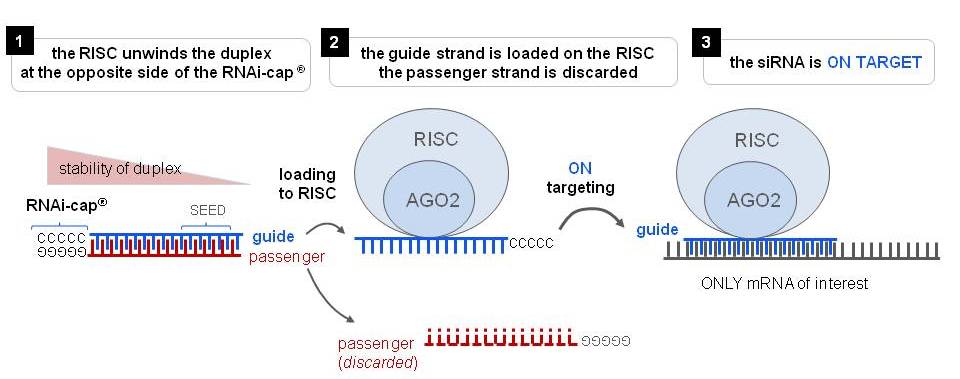



Riboxx Rna Technologies Benefits Of Rnai Cap For Sirna




Small Interfering Rna Wikipedia




A Simple And Cost Effective Approach For In Vitro Production Of Sliced Sirnas As Potent Triggers For Rnai Molecular Therapy Nucleic Acids




2 O Methyl At Mer Guide Strand 3 Termini May Negatively Affect Target Silencing Activity Of Fully Chemically Modified Sirna Sciencedirect




Seed Mediated Rna Interference Of Androgen Signaling And Survival Networks Induces Cell Death In Prostate Cancer Cells Molecular Therapy Nucleic Acids



The Sirna Non Seed Region And Its Target Sequences Are Auxiliary Determinants Of Off Target Effects




Aspsirna A Resource Of Asp Sirnas Having Therapeutic Potential For Human Genetic Disorders And Algorithm For Prediction Of Their Inhibitory Efficacy G3 Genes Genomes Genetics




Seed Dependant Off Target Effect The Capability Of Sirnas To Induce Download Scientific Diagram




Shrna And Sirna Of The Same Sequence Regulate The Same Subset Of Download Scientific Diagram



Sidirect




Seedseq Off Target Transcriptome Database




Seedseq Off Target Transcriptome Database




Small Interfering Rna Wikipedia




Tolerance For Mismatches Between An Sirna And Its Target Sirna Seed Download Scientific Diagram
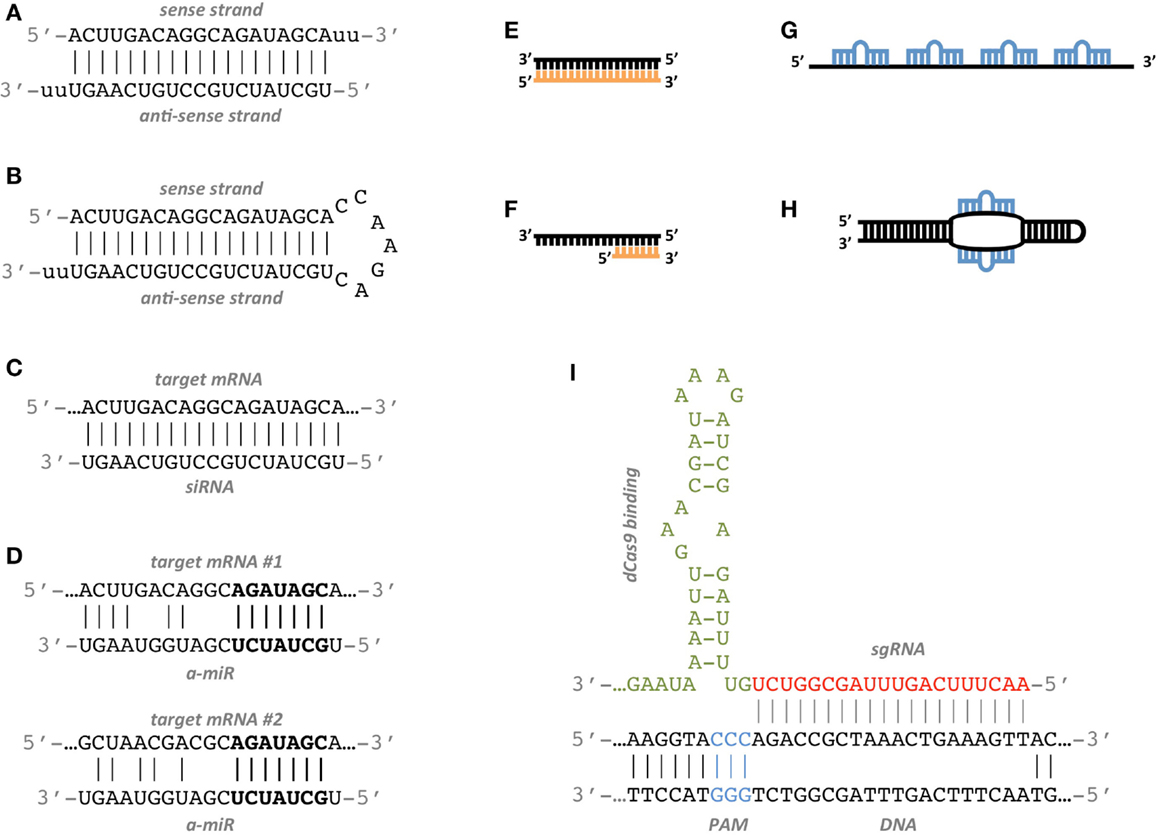



Frontiers Synthetic Rnas For Gene Regulation Design Principles And Computational Tools Bioengineering And Biotechnology




Graphical Representation Of Sirna Molecule A Sirna Duplex With Download Scientific Diagram



Designing Of Highly Effective Complementary And Mismatch Sirnas For Silencing A Gene



The Sirna Non Seed Region And Its Target Sequences Are Auxiliary Determinants Of Off Target Effects




Pdf Interactions Between The Non Seed Region Of Sirna And Rna Binding Rlc Risc Proteins Ago And Trbp In Mammalian Cells



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿